
ROLE OF THE LEAF
- convert light into food= photosythesis
- provide shade and camouflage for other organisms
- fallen leaves provide habitat+ food for decomposers ( ex. fungi&bacteria)
- add beauty to environment

- the epidermis is the external cells that protect the leaf from underneathe
- acts as a barrier to invaders such as fungi and bacteria
- cell margins fit tightly together
Secondary Structure: Cuticle
- since the epidermis is not completely waterproof, the cuticle performs this job
- a thin waxy covering on the top layer of leaves
- blocks gases through the cells of the epidermis
Result: both the cuticle+ epidermis are transparant= allows light through the leaf
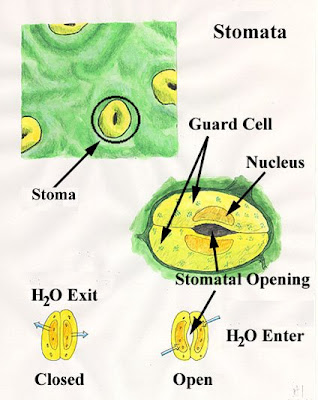
STOMATA 
What is a stomata?
- allows gases to enter and leave for photosynthesis ( process of which plants make their own food) and cellular respiration ( the air we breathe)
- stomata is an opening or pore in leaves that is surrounded by guard cells
- stomata are tiny holes within the epidermis
Secondary Structure: Guard Cells
- work together in pairs and possess thick walls
- large opening of stomata= faster the leaf can exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
SPONGY LAYER

Located beneath the palisade layer, its cells are irregular in shape and loosely packed. Although they contain a few chloroplasts, their main function is the temporary storage of sugars and amino acids synthesized in the palisade layer. They also help in the exchange of gases between the leaf and the environment. During the day, these cells give off oxygen and water vapor to the air spaces that surround them. They also pick up carbon dioxide from the air spaces. The air spaces are interconnected and open to the outside through the stomata (singular stoma).
VASCULAR TISSUE 
What is a vascular tissue?
- found in the veins of a leaf which consists of xylem ( transports water& minerals from roots-->stem--->leaves) & phloem ( transports sugar/food)
- veins conduct water & dissolved minerals in and out of the leaf
- to secure CO2 and release O2
(and the reverse in the dark)
Veins in a leaf perform 3 fluid- conducting functions
- conduct water into the leaf
- conduct dissolved minerals into the leaf
- conduct dissolved carbohydrates ( nutrients) out of the leaf
Secondary Structures
- leaf cells produce food by photosynthesis= dissolved carbohydrates exits the leaf= food is brought to the non-photosynthesizing parts of the plant
PALISADE CELLS

- palisade cells are found in leaves
- produce sugars by photosynthesis
- contain lots of chloroplasts to absorb light
- cells are block shaped so that many can be packed into the leaf
- top layer is exposed to the light & bottom layer is exposed to the gases in the spongy layer= energy + raw materials are available to each cell= maximizes light to make photosynthesis work

No comments:
Post a Comment