
ROLE
- keep the plant in the soil
- hold the stem in place
- holds the soil to prevent erosion ( water washes away soil)

FUNCTION
- brings nutrients in the plant
- Roots absorb water by photosynthesis and replace water by transpiration
- Roots absorb dissolved minerals and regulate the quantity of these minerals entering the rest of the plant
- Roots store starch made from the food produced by the leaves. Some of this stored food is used by the cells of hte root itself= transported to other plant parts that require it
SECONDARY STRUCTURES
- outer surface of root= absorbing function
- root systems are divided and subdivided into networks of roots to increase surface area
- roots absorb the most when their external surface area is enlarged

EPIDERMIS
- protects + enclose the interior root structures
- absorb water and dissolved minerals from soil
- root hairs enlarge surface area for absorption
- perform cellular respiration= food

SECONDARY STRUCTURES
- contain no chloroplasts= can't make food
- glucose used for cellular respiration comes from starch stred in the cortex layer of the root
CORTEX
- contain large vacuoles for food storage
- vacuoles are made from starch= consists of carbohydrate made by leaves
- cortex makes up a proportion of the volume of the root, particularly in young roots, where it functions in the transport of water and ions from the epidermis to the vascular (xylem and phloem) tissues. In older roots it functions as a storage tissue

ENDODERMIS 
ROLE
- determines what enters the vascular system for tranport to the rest of the plant
SECONDARY STRUCTURES
- special cells in the endodermis makes sure that materials in the centre of the root are filtered
- filtering keeps harmful substances out= allowing nutrients and water into the root's vascular tissue= nutrients and water transports to the rest of the plant
- selectively permeable membrane of an endodermis cell= pathway into the root's vascular tissue
- membrane of an endodermis cell= blocks passage of large particles which get through the endodermis if the cell membrane selects them= endodermis makes sure which minerals and how much of it gets through the vascular tissue at the centre of the root
VASCULAR TISSUE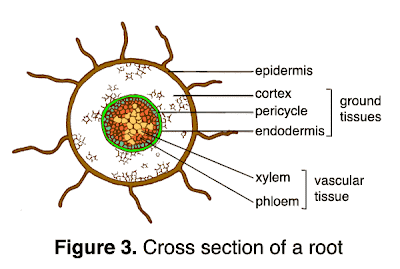
SECONDARY STRUCTURES
- vascular cylinder= contains both phloem + xylem
- xylem= transport water+ minerals+ other dissolved materials absorbed by the root to the upper parts of the plant
- phloem= conduct dissolved food
- phloem conducts dissolved food into the root= leaves manufactre extra glucose
- phloem conducts dissolved food out of the root and upward into the plant's stem and other structures= food storage
In result
- xylem= conducts water and minerals from the roots upward and throughout the plant
- phloem= transports dissolved foods in all directions within the plant.

No comments:
Post a Comment